Before you start
You need to have your logging set up to capture interactions between your LLM and users before you can evaluate them. To do so, you would need to integrate Maxim SDK into your application.
Evaluate any component of your trace or log to gain insights into your agent's behavior.
As your AI application grows in complexity, it becomes increasingly difficult to understand how it is performing on different flows and components. This granular insight becomes necessary to identify bottlenecks or low quality areas in your application's or agent's flow. By targeting the underperforming areas, you can optimize overall performance more effectively than using brute force approaches.
This is where Node level evaluation can help out. It enables you to evaluate a trace or its component (a span, generation or retrieval) in isolation. This can be done via the Maxim SDK's logger using a very simple API. Let us see how we can start evaluating our nodes.
Before you start
You need to have your logging set up to capture interactions between your LLM and users before you can evaluate them. To do so, you would need to integrate Maxim SDK into your application.
Two actions are mainly required to evaluate a node:
Once you have attached evaluators and variables to them, we will process the evaluator and display the results in the Evaluation tab under the respective node.
Missing variables message (although we will still process the evaluator even if variables are received after 5 minutes).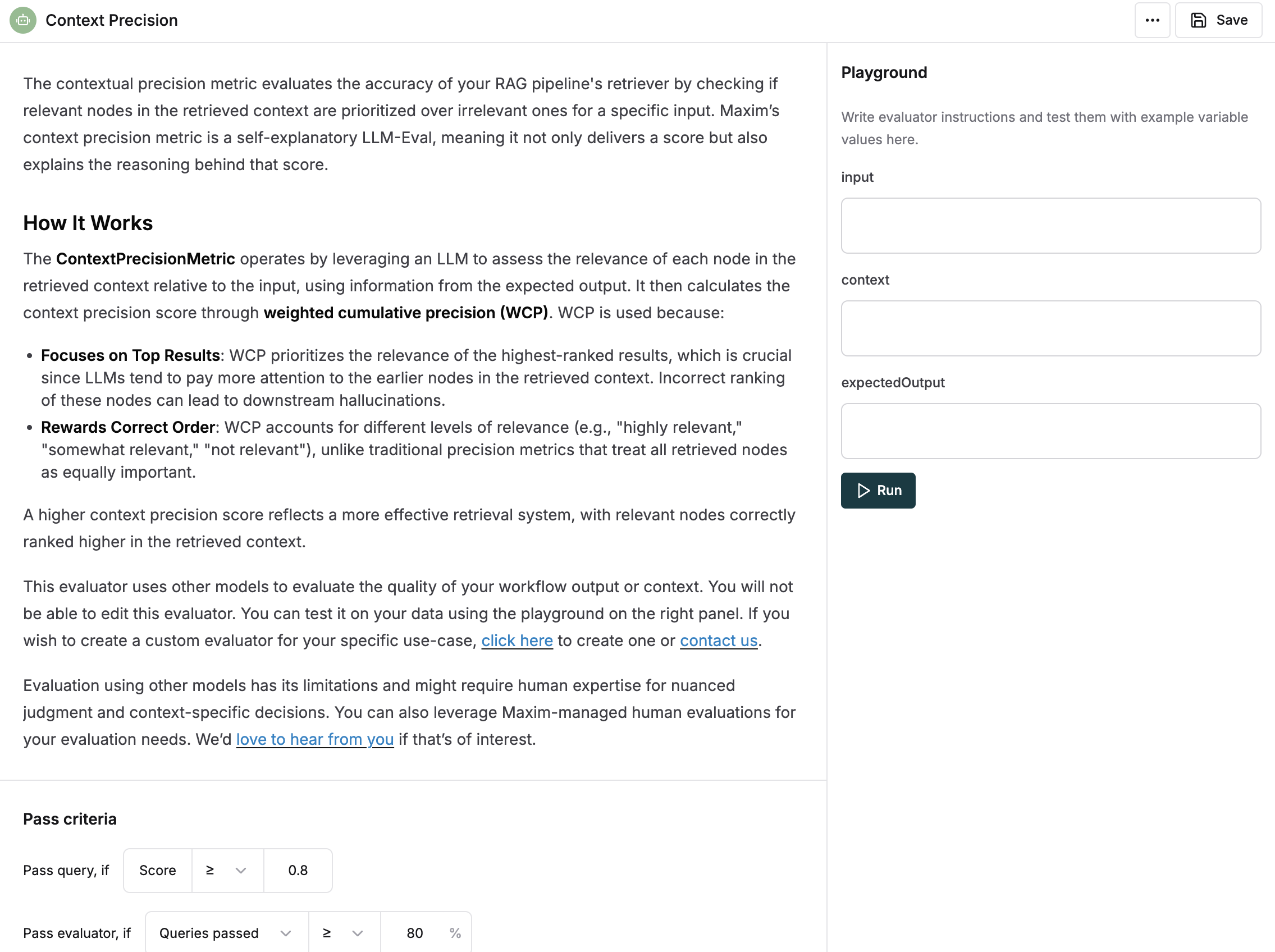
As per the image above, we can see that the evaluator needs
input,contextandexpectedOutputvariables.
We use the withEvaluators method to attach evaluators to any component within a trace or the trace itself. It is as easy as just listing the names of the evaluators you want to attach, which are available on the platform.
component.evaluate.withEvaluators("evaluator");
// example
generation.evaluate.withEvaluators("clarity", "toxicity");If you list an evaluator that doesn't exist in your workspace but is available in the store, we will auto install it for you in the workspace.
If the evaluator is not available in the store as well, we will ignore it.
Once evaluators are attached to a component, variables can be passed to them via the withVariables method. This method accepts a key-value pair of variable names to their values.
You also need to specify which evaluators you want these variables to be attached to, which can be done by passing the list of evaluator names as the second argument.
component.evaluate.withVariables(
{ variableName: "value" }, // Key-value pair of variables
["evaluator"], // List of evaluators
);
// example
retrieval.evaluate.withVariables(
{ output: assistantResponse.choices[0].message.content },
["clarity", "toxicity"],
);You can directly chain the withVariables method after attaching evaluators to any component. Allowing you to skip mentioning the evaluator names again.
trace.evaluate
.withEvaluators("clarity", "toxicity")
.withVariables({
input: userInput,
});This is very similar to Making sense of evaluations on logs, except that the evaluations for each component appear on their own card as it did for the trace.
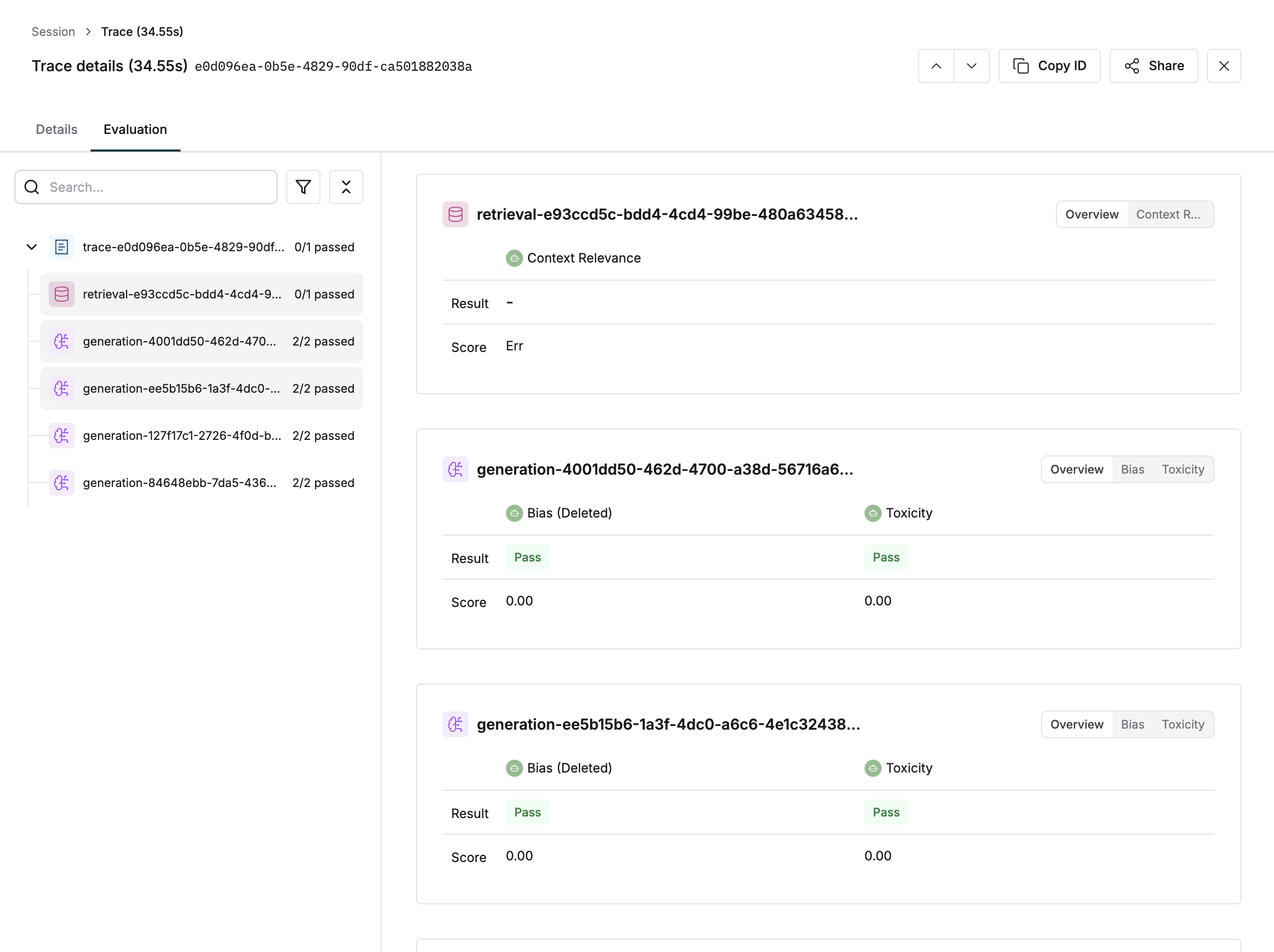
This example displays how Node level evaluation might fit in a workflow.
// ...previous flow
const generation = trace.generation({
id: uuid(),
messages: [
{
role: "system",
content: `You are a helpful assistant that helps people with their questions`,
},
],
model: "gpt-4o",
provider: "openai",
modelParameters: {
temperature: 0.7,
topP: 1,
maxTokens: 100,
},
name: "user-facing-chatbot",
});
// ...user message received
generation.addMessages([
{
role: "user",
content: userMessage,
},
]);
generation.evaluate
.withEvaluators("clarity", "toxicity")
.withVariables({
input: userMessage,
});
// ...retrieve and process context
generation.evaluate.withVariables(
{ context: context },
["toxicity"], // only toxicity requires context
);
// ...generate response
generation.result(llmResponse);
generation.evaluate.withVariables(
{ output: llmResponse.choices[0].message.content },
["clarity", "toxicity"],
);
// ...flow continues